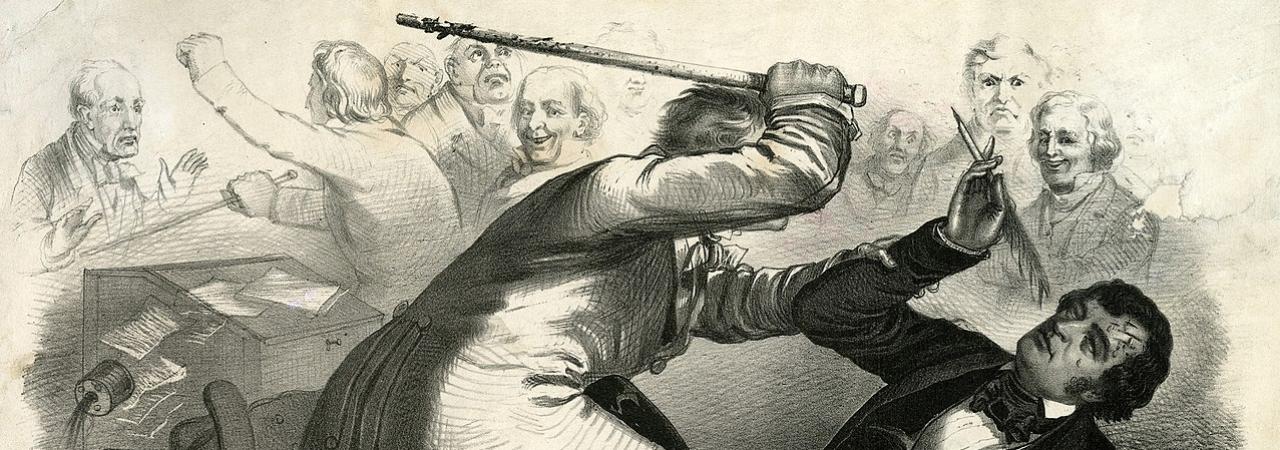
Political caricature of the caning of Charles Sumner, which occurred on May 22, 1856, depicting Sumner on the floor as Preston Brooks lunges at him in retaliation for a speech given by Sumner criticizing slaveholders.
The American Civil War is well-known for the primary reason that it started– the institution of slavery. The bloody and costly war that raged for four tumultuous years affected the lives of all people in the North and South. Over 600,000 people were killed over the course of the war, about 500 people per day. The violent conclusion of the Civil War, however, was decades in the making. All-encompassing sectional differences on the issue of slavery, such as outright support/opposition of slavery, economic practices, religious practices, education, cultural differences, and political differences kept the North and South at near constant opposition to one another on the issue of slavery. Gradually, throughout the beginning of the nineteenth century, the North and South followed different paths, and developed into two distinct and very different parts of the United States.
The North: A Titan of Industry
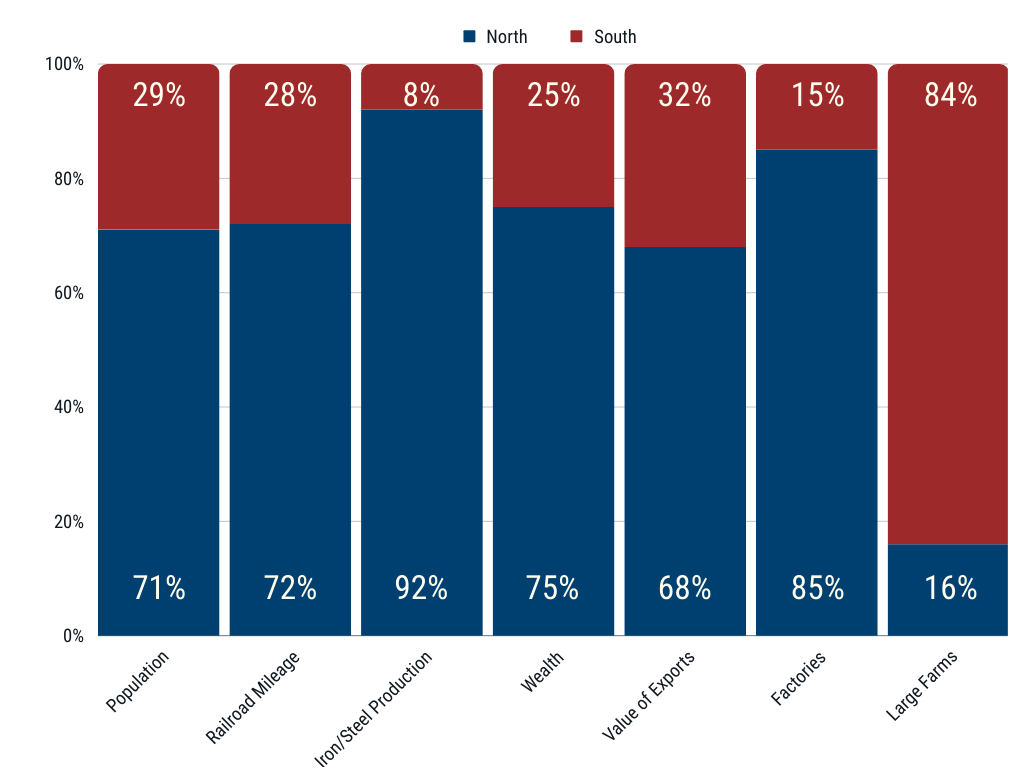
The antebellum Northern United States was recognized by its tight-knit immigrant communities and industrial might. In the North, the soil and climate favored smaller farmsteads rather than large plantations, which did not need slavery to operate them. Industry and manufacturing might flourished, which was fueled by European immigrant labor. Natural resources such as iron and copper were more abundant in the North than in the South. Many large cities were established such as Philadelphia, Pittsburgh, New York City, Boston, Cleveland, Cincinnati, Chicago, Milwaukee, and Detroit to better transport these natural resources around the country and manufacture them into goods. New York City was the largest city with more than 800,000 inhabitants. By 1860, one quarter of all Northerners lived in urban areas. Between 1800 and 1860, the percentage of laborers working in agricultural pursuits dropped drastically from 70% to only 40%, and conversely increased in manufacturing. The institution of slavery had virtually died out in the North. Slave labor was replaced in the cities and factories by immigrant labor from Europe. An overwhelming majority of immigrants, seven out of every eight, settled in the North rather than the South because of better job opportunities in manufacturing. Transportation was easier in the North, which boasted more than two-thirds of the railroad tracks in the country, as well as a labyrinth of waterways that connected the entire Northern region.

Far more Northerners than Southerners belonged to the Whig/Republican political party, and they were far more likely to have careers in business, medicine, or education. In fact, an engineer was six times as likely to be from the North than from the South. Northern children were slightly more prone to attend school than Southern children. Religion in the North was different than the South. The North used religion as a means to denounce slavery and call it a moral evil and teamed up politically with abolitionists and politicians to bring an end to slavery.
The South: An Agricultural Aggregate
The antebellum Southern United States is noted for its vast farmland, aristocratic-like social structure, and the use of chattel slavery to yield high agricultural profits. The fertile soil and warm climate of the South made it ideal for large-scale farms to grow crops like tobacco and cotton. Because agriculture was so profitable, few Southerners saw a need for industrial development. Eighty percent of the labor force worked on a farm or plantation. Although two-thirds of Southerners owned no slaves at all, by 1860, the South's "peculiar institution" was inextricably tied to the region's economy and culture. In fact, there were almost as many blacks, both enslaved and free, in the South as there were whites (4 million blacks and 5.5 million whites). Virginians owned the most slaves out of any state, with a total of 490,865 slaves. There were no large-scale industrial cities in the South as there were in the North. The only cities that could compare to the smallest Northern cities were New Orleans, Richmond, Charleston, Atlanta, and Mobile. Most of the cities that were located on rivers and coastlines acted as shipping ports to send agricultural produce to European or Northern markets.

Only one-tenth of Southerners lived in urban areas. The most populated city in the South was New Orleans, Louisiana with a population of 168,675. Transportation between cities and across the South was extremely difficult, except by water. Only 35% of the nation's train tracks were located in the South. Waterways proved useful to Southern port and river cities, but an overwhelming amount of inland transportation was underdeveloped in the South.
A slightly smaller percentage of white Southerners were literate than their Northern counterparts, and Southern children tended to spend less time in school. This was due to the cultural tie to the farms, and children were needed by the family to help on farms or around the home. As adults, Southern men tended to ally with the Democratic political party and gravitated toward military careers as well as agriculture. Religiously, the South used religion to support the institution of slavery, citing various Bible verses to further their ideology.
What Led to Disunion?
Ultimately, what led to the American Civil War were the differences in the North and South's views toward the institution of slavery. There were other aspects within the institution of slavery that led to division in the United States. Economic practices, religious practices, education, cultural differences, and political differences all furthered the division between the North and South about the institution of slavery. These decade-long divisions all culminated in the bloody conflict of the Civil War, which permanently ended the division and abolished slavery permanently.