African Americans in the Armed Forces Timeline
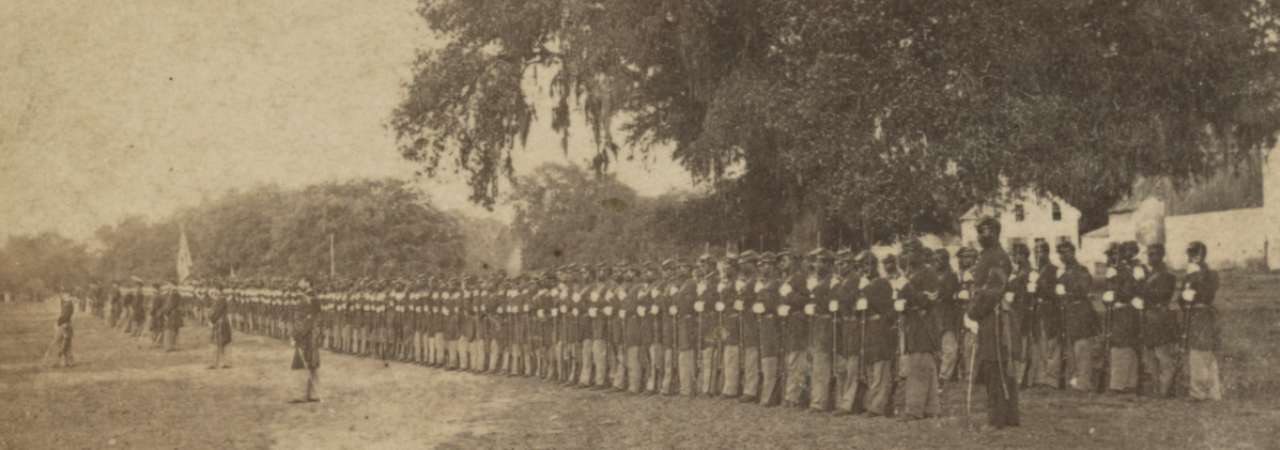

Civil 29th Regiment, Connecticut Volunteers, U.S. Colored Troops, in formation near Beaufort, S.C., where Cooley lived and worked. It was Connecticut’s first African American regiment.
The timeline below details the actions of African Americans in the armed forces from the Revolutionary War until the end of the Civil War.
Revolutionary War War of 1812Civil War
Revolutionary War
1770
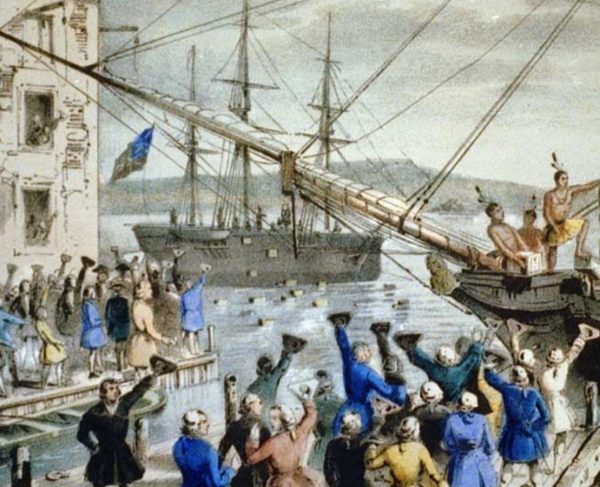
- March 5 - Crispus Attucks, a Bostonian sailor who had escaped slavery, one of 5 victims of the Boston Massacre, is killed
1775
- November - Virginia’s British Royal Governor, Lord Dunmore, issued a proclamation that he would free any slave who left his master to serve alongside British forces. Within a month 300 had joined what Dunmore dubbed his “Ethiopian Regiment.”
1776
- December 25 - The 14th Continental Regiment, an integrated unit organized by John Glover, manned the boats that ferried the Continental Army across the Delaware River.
1777
- January 3 - The 11th Continentals, including at least two black Marines listed on regimental muster rolls as "Isaac Walker" and "Orange," participate in the Battle of Princeton, in a counterattack that George Washington personally led from the saddle of a battle-nervous white horse. The victory helped turn the tide of the Revolution.
1778
- The 1st Rhode Island Regiment is established. The most famous integrated fighting unit during the Revolutionary War, 88 slaves enlisted alongside white Patriots. The men were guaranteed freedom at the end of their service. The Rhode Island State Assembly promised compensation to their former masters.
1781
- October - James Armistead Lafayette, a slave who received permission from his master, William Armistead, to enlist in the Marquis de Lafayette’s French Allied units, played a pivotal role during the Battle of Yorktown, revealing British positions to American generals.
1787
- James Armistead Lafayette is finally granted his freedom through service to the United States after the Marquis de Lafayette wrote a letter to Congress on his behalf.
War of 1812
1812
- At the outbreak of the war, many northern states had abolished slavery. The US military was still segregated, and it was difficult to enlist. Many freedmen opted to serve in the US Navy, as it was an integrated service. Joshua Barney's “Mosquito Squadron” was one of the most famous of those fleets, each ship containing a crew of veteran sailors, including enslaved and free African Americans,
1814
- April 2 - Sir Alexander Cochrane, Vice Admiral and Commander in Chief of His Majesty’s Ships and Vessels in North America issues a proclamation stating that those who served in the King’s forces would be liberated after the war.
- May 18 - The Corps of Colonial Marines is officially organized. The British-trained regiment saw their first bout of combat two weeks later, participating in a British raid up Pungoteague Creek. Eventually, 3,600 African Americans joined the British military effort, with between 550 and 700 trained as troops.
Civil War
1861
- April - The Civil War begins; free African Americans in the North trying to enlist in the Union Army are turned away.
1862
- April 16 - Congress abolishes slavery in the District of Columbia.
- September 22 - Abraham Lincoln issues the Preliminary Emancipation Proclamation.
- October 29 - African American soldiers skirmish with Confederates at Island Mound, Missouri.
1863
- January 1 - The Emancipation Proclamation goes into effect, freeing the slaves in the territory in active rebellion against the government.
- May 21 - July 9 - Eight African American regiments take part in the Battle of Port Hudson.
- May 22 - War Department General Order No. 143 establishes the United States Colored Troops.
- July 1 - First Kansas Colored Volunteers fight in the Battle of Cabin Creek.
- July 18 - 54th Massachusetts assaults Fort Wagner near Charleston, South Carolina; Sgt. William Carney becomes the first African American to receive the Medal of Honor.
- December - Robert Smalls, a former slave from Charleston, becomes the first and only African American to be commissioned a captain in the U.S. Navy during the Civil War.
1864
- April 12 - Fort Pillow massacre in western Tennessee.
- June 15 - Congress passes a bill authorizing equal pay, equipment, arms, and healthcare for African American troops.
- September 29 - Battle of Chaffin's Farm, Virginia. Fourteen U.S.C.T. earn the Medal of Honor.
1865
- February 1 - Abraham Lincoln signs the 13th Amendment, abolishing slavery throughout the United States.
- June 19 - Enslaved African Americans in Texas are the last to learn of their emancipation. The day is celebrated thereafter as Juneteenth.
Topic(s):